
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
| Claims made in "Joseph Smith and the Biblical Test of a Prophet" | A FAIR Analysis of: Watchman Fellowship, a work by author: Rick Branch
|
Claims in "Testing the Book of Mormon by Moroni 10:4" |
| Claim Evaluation |
| Watchman Fellowship |
|
Jump to details:
Author's quote: “While there continues to be mounting evidence for the historicity of the biblical record, the Book of Mormon is still seeking that first authenticated scrap of evidence.”
Author's sources:
What do we find in Mesoamerican archaeology with respect to toponyms [toponyms = place names, such as city names]? First, unlike the biblical lands where many toponyms survived due to a continuity of culture, there is no reason to assume that Maya languages and Nephite languages were related. Secondly, we find that toponyms often disappeared from one era to the next. Many of the Mesoamerican cities today have Spanish names such as San Lorenzo, La Venta, and El Mirador. The “collapse of the indigenous civilizations before the conquistadors created a sharp historical discontinuity. We have the names of almost none of the Classic Mayan and Olmec cities of two millennia ago, which is why they are known today under Spanish titles such as La Libertad and Tres Zapotes, Santa Rosa and El Mirador.”[1] Archaeologists simply don’t know what many of the original names for these Mayan cities were. If archaeologists don’t know the names of some cities they have discovered, how could one expect to provide English names for those cities, such as names provided in the Book of Mormon?[2]
Additionally, scholars are uncertain as to the pronunciation of Mesoamerican cities for which they do have names. This is because city-inscriptions are often iconographic, and not all scholars agree that such icons represent city names. These icons are not only rare (as noted above) but they are symbolic rather than phonetic. In other words, when archaeologists find an iconographic inscription designating a place as the Hill of the Jaguar, the pronunciation of this inscription would be dependent on the language of the speaker—be it a Zapotec, a Mixtec, or a Nephite.[3] The only way to identify an ancient site is by way of an inscription giving a phonetically intelligible name. Barring further discoveries, we may never know how the names of Mesoamerican cities were pronounced in Book of Mormon times.
If the epigraphic [e.g., inscriptions on stones or monuments] data from the Old World were as slim as the epigraphic data from the New World, scholars would be severely limited in their understanding of the Israelites or early Christianity. It would likely be impossible, using strictly non-epigraphic [i.e., non-written, non-language based] archaeological evidences, to distinguish between Canaanites and Israelites when they co-existed in the pre-Babylonian (pre-587 B.C.) Holy Land.[4] We find that the same problems would be apparent in the study of early Christianity if scholars were faced with the absence of epigraphic data. For instance, if Diocletian’s persecutions of Christianity had been successful, if Constantine had never converted, and if Christianity had disappeared around A.D. 300, it would be very difficult if not impossible to reconstruct the history of Christianity using nothing but archaeological artifacts and imperial Roman inscriptions.[5]
“It is quite possible,” notes Hamblin, “for a religion, especially an aniconic religion [a religion which does not use written, symbolic images], to simply disappear from the archaeological record. Despite the fact that there were several million Christians in the Roman [E]mpire in the late third century, it is very difficult to [discover] almost anything of substance about them from archaeology alone.”[6]
Did you know that one of the very few ancient cities in Mesoamerica for which the pre-Columbian name is known is named "Lamanai"? It means "submerged crocodile." According to Wikipedia, "The site's name is pre-Columbian, recorded by early Spanish missionaries, and documented over a millennium earlier in Maya inscriptions as Lam'an'ain." Read about it in Wikipedia: Lamanai. We're not saying that this is a Book of Mormon city, but the name makes you think.
Given the inherent advantages (cultural continuity, toponyms, environmental conditions which favor the preservation of artifacts, time and resources invested in archaeological and linguistic field-work, etc.) of Old World studies compared to New World studies, it is interesting to note some recently discovered correlations between the early chapters of the Book of Mormon and the archaeological record of the Old World in ways that would have been unknown at the time the book was translated. In other words, it is impossible that Joseph Smith could have known any of the Old World archaeological data that have come to light since his death—these finds do not contradict the Book of Mormon and, in many instances, are consistent with its stories.
Consider, for instance, a recently discovered altar in Yemen that is consistent with a story related in the Book of Mormon. This altar, discovered by non-LDS archaeologists, has the tribal name of NHM carved into it. The altar is located in the same vicinity in which the Book of Mormon describes the Lehites stopping in Nahom to bury Ishmael, and dates from the same time period.[7] One should here remember that the Hebrew language of Nephi's era has no written vowels, and thus NHM could very likely be “NaHoM.”[8] The name NHM does not just appear out of thin air either, but rather the location of an ancient NHM exists not only within the specific time of the Lehite journey, but also within a plausible location through which LDS scholars believe the Lehites traveled in Arabia before embarking on their voyage to the New World.
| Main article: | Nahom |
It is also worth noting that there is a growing body of evidence from New World archaeology that supports the Book of Mormon. For example, results from LiDAR surveys in Mesoamerica continue to reveal infrastructure consistent with Book of Mormon history.[9]
Dr. John Clark of the New World Archaeological Foundation compiled a list of sixty items that are mentioned in the Book of Mormon and were publicly criticized in Joseph Smith's day and matched it with the best research available at that time. The list includes items such as “steel swords,” “barley,” “cement,” “thrones,” and literacy. In 1842, only eight (or 13.3%) of those sixty items were confirmed by archaeological evidence. Thus, in the mid-nineteenth century, archaeology provided little support for the claims made by the Book of Mormon. In fact, the Book of Mormon text ran counter to both expert and popular ideas about ancient America in the early 1800s.
As the efforts of archaeology have shed light on the ancient New World, we find in 2005 that forty-five of those sixty items (75%) have been confirmed. Thirty-five of the items (58%) have been definitively confirmed by archaeological evidence and ten items (17%) have received possible—tentative, yet not fully verified—confirmation. Therefore, as things stand at the moment, current New World archaeological evidence tends to verify the claims made by the Book of Mormon.[10]
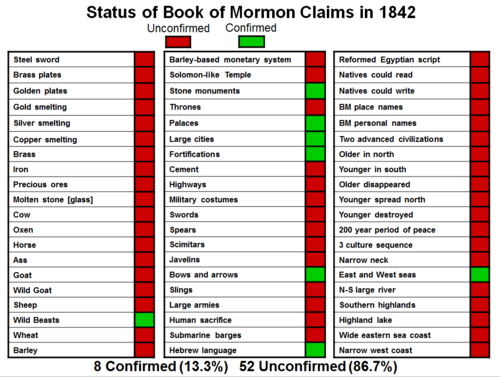
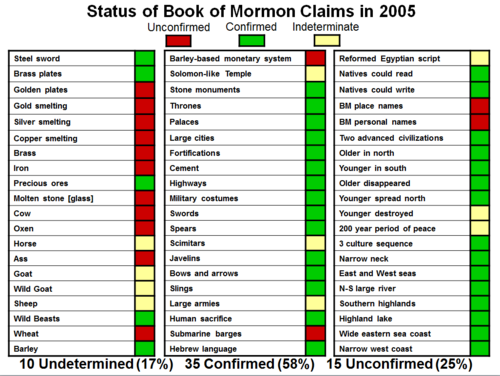
These charts are criticized for “not including all anachronisms” and some claims surface occasionally that Dr. Clark “didn’t follow the consensus on these items”. Critics have prepared charts of their own using their own methodologies to try and “debunk” Clark’s chart. These criticisms miss the entire point of the charts, are ignorant of the methodology by which they were created, and ignore who Dr. Clark is. The selection of the anachronisms was done by taking a random sample of the publicly documented claims of anachronisms from Joseph Smith's day. Dr. Clark is one of the most well-recognized and esteemed Mesoamericanists currently working in his field. He (along with Wade Ardern and Matthew Roper) carefully prepared these lists using the best contemporary scholarship to show the trend that Book of Mormon anachronisms follow—expiring over time (1 Corinthians 4:5). Unfortunately the research they marshaled was never published since such wasn’t the aim of the presentation.
Matthew Roper presented updated charts at the 2019 FairMormon Conference. He updated the list that Clark first made to include 205 publicly availble claims of anachronisms in the Book of Mormon. His research concludes that 141 items have been confirmed, 26 items are trending, and 38 remain yet unconfirmed.[11]
More information on anachronisms can be found in the articles addressing anachronisms, research presented at FairMormon Conferences, and other Latter-day Saint academic venues.
Ambiguous statements and grandiose claims have appeared in numerous LDS and RLDS journals, but, to date, not a single claim has been substantiated.
Author's sources:
- Zarahemla Record, August 1989 p. 7 ("The massive fortification of the site dating around AD 825 surpass anything found in Maya archaeology to date. The Book of Mormon description in Mormon 4:10 is being confirmed.")
Sectarian critics who accept the Bible, but not the Book of Mormon, sometimes claim that the Bible has been "proven" or "confirmed" by archaeology, and insist that the same cannot be said for the Book of Mormon.
The claim that, unlike the Bible, there is no archaeological evidence supporting the Book of Mormon is based on naive and erroneous assumptions. Without epigraphic New World evidence (which is currently extremely limited from Book of Mormon times), we are unable to know the contemporary names of ancient Mesoamerican cities and kingdoms. To dismiss the Book of Mormon on archaeological grounds is short-sighted. Newer archaeological finds are generally consistent with the Book of Mormon record even if we are unable (as yet) to know the exact location of Book of Mormon cities.
Note: Many of the topics sometimes addressed in archaeological critiques of the Book of Mormon are treated in detail on the Book of Mormon "anachronism" page.
A reasonable question for those suggesting that there is no archaeological evidence for the Book of Mormon would be “What archaeological evidence might be considered the minimal irrefutable proof needed to convince a non-believing world of the authenticity of the Nephite scripture?”
Some people might suggest that finding the existence of horses or chariots would constitute proof for the Book of Mormon. This is doubtful. Finding such items would merely demonstrate that such things existed in the ancient New World, and while such discoveries may be consistent with the Book of Mormon, they hardly amount to “proof.”
As an example, the Book of Mormon mentions barley which, until recently, was thought not to exist in the ancient Americas. Critics considered barley to be one of the things that “Joseph Smith got wrong.” However, pre-Columbian New World barley has now been verified, without people flocking to join the Church because of this discovery. For critics, finding such items are too often seen as “lucky guesses” on the part of Joseph Smith. The Book of Mormon mentions cities, trade, warfare, towers, and the use of armor—all of which did exist in the ancient Americas—yet their existence has not convinced critics that the Book of Mormon is an authentic ancient text.
When examining ancient evidence archaeologists work with a very fragmentary record. In general, they find physical evidence, but such evidence in and of itself doesn’t provide much information unless it is placed within a context—a framework by which it can be understood. For instance, if an archaeologist finds a pot (or, more likely, a fragment of a pot), it provides little evidence concerning the civilization that created or used the pot. Contextual clues—such as other artifacts uncovered near the pot—may provide some clues about the timeframe in which the pot was last used, but it certainly doesn’t provide conclusive evidence as to what the civilization, or the individuals in that civilization, were like.
Critics, for example, sometimes deride the idea that Nephites were, for much of their written history, “Christians.” In the critics' view, there should be archaeological remains indicating a Christian presence in the ancient New World. How, exactly, would an archaeologist distinguish a Christian's pot from that of a non-Christian? What would a Christian pot look like? One must also keep in mind that, according to the Book of Mormon, the New World “Christians” were a persecuted minority who were wiped out over fifteen hundred years ago. How much archaeological evidence would we really expect to have survived the intervening centuries?
For the archaeologist, the strongest contextual clues come from writing or markings that are sometimes found on the physical evidence. These are of two general types: epigraphic and iconographic. Epigraphic evidence consists of a written record, such as this text you are reading, while iconographic evidence consists of pictures, or icons. For instance, the word “cross” is epigraphic, but a picture of a cross is iconographic. Epigraphic evidence, providing it can be translated, provides a record of what people thought or did. Iconographic evidence is much more symbolic and its interpretation depends on the context in which the image is used.
As noted by Dr. William Hamblin, "the only way archaeologists can determine the names of political kingdoms, people, ethnography, and religion of an ancient people is through written records."
"Iconography can be helpful, but must be understood in a particular cultural context which can only be fully understood through written records. (Thus, the existence of swastikas, for example, on late medieval mosques in Central Asia or on Tibetan Buddhist temples in Tibet does not demonstrate that Muslims and Buddhists are Nazis, nor, for that matter, that Nazis are Buddhists. Rather, medieval swastikas demonstrate that different symbolic meanings were applied to the same symbol in early twentieth century Germany, Muslim Central Asia, and in Tibet.)"[12]
Many ancient peoples, however, wrote on perishable materials that have deteriorated through the centuries. Egypt, for example, wrote on materials that have survived through the ages, whereas the kingdom of Judah generally did not.
"[F]rom archaeological data alone," notes Hamblin, "we would know almost nothing about the religion and kingdom of ancient Judah. Indeed, based on archaeological data alone we would assume the Jews were polytheists exactly like their neighbors. Judaism, as a unique religion, would simply disappear without the survival of the Bible and other Jewish written texts."
"...Methodologically speaking, does the absence of archaeologically discovered written records demonstrate that a certain kingdom does not exist? Or to put it another way, does the existence of an ancient kingdom depend on whether or not twenty-first century archaeologists have discovered written records of that kingdom? Or does the kingdom exist irrespective of whether or not it is part of the knowledge horizon of early twenty-first century archaeologists? Or, to state the principle more broadly, does absence of evidence equal evidence of absence?"[13]
Understanding that a written record (epigraphic or iconographic) is necessary for building archaeological context, what do we find when we turn to the records of the ancient (i.e. before A.D. 400) Americas?
Of the approximately half dozen known written language systems in the New World (all of which are located in Mesoamerica), only the Mayan language can be fully read with confidence. Scholars can understand some basic structure of some of the other languages, but they cannot fully understand what the ancients were saying. In other words, there is a problem with deciphering the epigraphic record. According to the experts, “the pronunciation of the actual names of the earliest Maya kings and other name-glyphs from other writing systems is not known with certainty.”[14]
For the time period in which the Nephites lived, scholars are aware of only a very limited number of inscriptions from the entire ancient New World that can be read with any degree of certainty. Even with these fragments, however, scholars are still uncertain from these inscriptions just how the ancients pronounced the proper names and place names (toponyms). Four of these readable inscriptions merely give dates or a king’s name—a very limited cultural context. Another five inscriptions contain historical information and proper names—the mention of the cities Tikal and Uaxactun (for which the ancient pronunciation remain uncertain) and five kings from these two cities (whom we know by iconographic symbols and whose ancient pronunciation remains uncertain).[15]
With such sparse epigraphic information, how could we possibly recognize—even if they we discovered archaeologically—that we had found the location of cities we know as Bountiful and Zarahemla, or if the religious rulers were actually named Nephi or Moroni? The critics like to claim that there is no archaeological evidence for the Book of Mormon, but the truth is that there is scant archaeological data to tell us anything about the names of ancient New World inhabitants or locations—and names are the only means by which we could archaeologically identify whether there were Nephites in ancient America.
Religious critics frequently like to compare the lack of archaeological support for the Book of Mormon with what they are certain is voluminous archaeological support for the Bible. There is a drastic difference, however, between the two worlds (Old and New) when it comes to epigraphic data, iconographic data, the continuity of culture, and toponyms.
We have already noted the dearth of readable New World inscriptions from Nephite times. From biblical lands, however, we know of thousands of contemporary inscriptions that have survived to modern times. We have pointed out that very few toponyms (place-names) can be read in the surviving few epigraphic fragments from the Nephite-era New World. In contrast, we find for the Bible lands not only scores of epigraphic records identifying ancient Mediterranean cities, but we also sometimes find a “continuity of culture” that preserves city names. In other words, many modern Near Eastern cities are known by the same name as they were known anciently (this is not the case for ancient America). Knowing the exact location of one city helps biblical archaeologists locate other cities, simply by calculating the distances.[16]
Even acknowledging the archaeological advantages for determining the location and historical actuality of biblical lands, we find that only slightly more than half of all place names mentioned in the Bible have been located and positively identified.[17] Most of these identifications are based on the preservation of the toponym. For biblical locations with no toponym preserved, only about 7% to 8% of them have been identified to a degree of certainty and about another 7% to 8% of them have been identified with some degree of conjectural certainty.[18] The identification of these locations without place names could not have been made were it not for the identification of locations with preserved toponyms. If few or no Biblical toponyms had survived in a continuous, unbroken "language chain" from the Bible's era to our own, the identification of biblical locations would be largely speculative.
Despite the identification of some biblical sites, many important Bible locations have not been identified. The location of Mt. Sinai, for example, is unknown, and there are over twenty possible candidates. Some scholars reject the claim that the city of Jericho existed at the time of Joshua. The exact route taken by the Israelites on their Exodus is unknown, and some scholars dispute the biblical claim that there ever was an Israelite conquest of Canaan.[19]

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now