
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
< Criticism of Mormonism | Books | The Changing World of Mormonism(Redirected from The Changing World of Mormonism/Index/Chapter 12)
| Chapter 11 | A FAIR Analysis of: The Changing World of Mormonism, a work by author: Jerald and Sandra Tanner
|
Chapter 13 |
| Claim Evaluation |
| The Changing World of Mormonism |
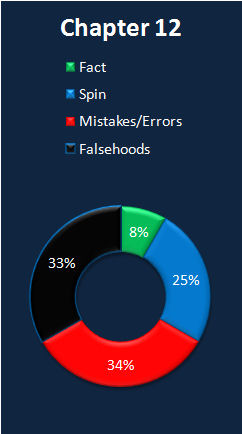
|
Jump to details:
The Bible has secondary status in the Mormon Church.
Joseph Smith taught that the Bible contains errors.Author's sources:
- Pearl of Great Price, p.59
"Bible, Inerrancy of," Gospel Topics on LDS.org,
The Latter-day Saints have a great reverence and love for the Bible. They study it and try to live its teachings. They treasure its witness of the life and mission of the Lord Jesus Christ. The Prophet Joseph Smith studied the Bible all his life, and he taught its precepts. He testified that a person who can “mark the power of Omnipotence, inscribed upon the heavens, can also see God's own handwriting in the sacred volume: and he who reads it oftenest will like it best, and he who is acquainted with it, will know the hand [of the Lord] wherever he can see it” (Teachings of the Prophet Joseph Smith, 56).
As the Bible was compiled, organized, translated, and transcribed, many errors entered the text. The existence of such errors becomes apparent when one considers the numerous and often conflicting translations of the Bible in existence today. Careful students of the Bible are often puzzled by apparent contradictions and omissions. Many people have also been curious about references by biblical prophets to books or scriptural passages that are not currently in the Bible.[1]
Latter-day Saints and the Bible |
|
Reliability of the Bible |
|
Creation |
|
Genesis |
|
Understanding the Bible |
|
Cultural issues |
|
The Bible and the Book of Mormon |
|
As Blake Ostler observed of the "Chicago Statement on Biblical Inerrancy":[2]
The doctrine of inerrancy is internally incoherent. In my opinion, numerous insuperable problems dictate the rejection of inerrancy in general and inerrancy as promulgated in the Chicago Statement in particular. First, the Chicago Statement is self-referentially incoherent. One cannot consistently assert that the Bible is the basis of his or her beliefs and then assert that one must nevertheless accept biblical inerrancy as asserted in the Chicago Statement...This statement contains a number of assertions, propositions if you will, that are not biblical. Inerrancy, at least as recently asserted by evangelicals, is not spelled out in the Bible. Nowhere do the words inerrant or infallible appear in the Bible. Such theoretical views are quite alien to the biblical writers. Further, inerrancy is not included in any of the major creeds. Such a notion is of rather recent vintage and rather peculiar to American evangelicalism. Throughout the history of Christian thought, the Bible has been a source rather than an object of beliefs. The assertion that the Bible is inerrant goes well beyond the scriptural statements that all scripture is inspired or "God-breathed." Thus inerrancy, as a faith commitment, is inconsistent with the assertion that one's beliefs are based on what the Bible says. The doctrine of inerrancy is an extrabiblical doctrine about the Bible based on nonscriptural considerations. It should be accepted only if it is reasonable and if it squares with what we know from scripture itself, and not as an article of faith... However, it is not and it does not.
The Chicago Statement can function only as a statement of belief and not as a reasonable observation of what we find in the Bible. The Chicago Statement itself acknowledges that we do not find inerrant statements in the Bible, for it is only "when all facts are known" that we will see that inerrancy is true. It is very convenient to propose a theory that cannot be assessed unless and until we are in fact omniscient. That is why the Chicago Statement is a useless proposition. It cannot be a statement of faith derived from the Bible because it is not in the Bible. It cannot be a statement about what the evidence shows because the evidence cannot be assessed until we are omniscient.[3]
Latter-day Saints do not subscribe to the conservative Protestant belief in scriptural inerrancy. We do not believe that any book of scripture is perfect or infallible. Brigham Young explained:
When God speaks to the people, he does it in a manner to suit their circumstances and capacities.... Should the Lord Almighty send an angel to re-write the Bible, it would in many places be very different from what it now is. And I will even venture to say that if the Book of Mormon were now to be re-written, in many instances it would materially differ from the present translation. According as people are willing to receive the things of God, so the heavens send forth their blessings.[4]
So while the Book of Mormon has come down to us with fewer doctrinal errors and corruptions than the Bible, even it could be improved if we were ready to receive further light and knowledge.
Infelicities of language are also to be expected when produced by revelators with little education, said George A. Smith:
The Book of Mormon was denounced as ungrammatical. An argument was raised that if it had been translated by the gift and power of God it would have been strictly grammatical.... When the Lord reveals anything to men, he reveals it in a language that corresponds with their own. If you were to converse with an angel, and you used strictly grammatical language he would do the same. But if you used two negatives in a sentence the heavenly messenger would use language to correspond with your understanding.[5]
It is claimed that Latter-day Saint leaders diminish the Bible as untrustworthy.
Do the Latter-day Saints detract from the Bible? Do they criticize it? No more so than the majority of Biblical scholars.
Early LDS leaders' views on the problems with biblical inerrancy and biblical translation would seem mainstream to most today. Only those who completely reject modern biblical textual criticism would find LDS leaders' views radical or evil. In fact, LDS beliefs on the matter accord well with many other Christian denominations. Those who vilify LDS belief on this point tend to be at the extreme end of the debate about scriptural inerrancy, and would also reject a modern creedal, orthodox scholar's views.
The Latter-day Saints believe that the Bible is true. It is inspired and inspiring, having been inspired by God and written by prophets, apostles, and disciples of Jesus Christ.
Prior to this publication, the Church purchased most of its King James Bibles from Cambridge University Press. Does this sound like an organization that is using the Bible merely as a public relations gimmick? If so, millions of members were never told. The Church and its members have a deep love and appreciation for the Word of God as found in the Bible.
The bold assertion that the LDS do not value the Bible is amusing. There is no presentation of statistics, only anecdotal claims that first, LDS members do not read the Bible and are not familiar with it, and second, that they constantly hear from their leaders that the Bible is less than trustworthy.
In a survey published in July 2001, Barna Research Group, Ltd. (BRG) made the following observations:
The study also revealed that barely half of all Protestant adults (54%) read the Bible during a typical week. Barna pointed out that Mormons are more likely to read the Bible during a week than are Protestants-even though most Mormons do not believe that the Bible is the authoritative Word of God.[6]
BRG is not affiliated with the LDS Church, nor was the LDS Church involved in the survey. Members of the LDS Church likewise would not categorize their faith in this fashion—they do, in fact, regard the Bible as authoritative and the Word of God. Yet the survey indicated that they certainly do read the Bible consistently. Also, over the course of two years out of every four years, every member of the Church is asked to read and study the entire text of the Bible as part of the Church's Sunday School curriculum. Asked by whom? By the leaders of the LDS Church.
One of the often-neglected events in LDS history happened in 1836. Joseph Smith arranged for a Hebrew scholar to come and teach Hebrew to the members of the LDS Church in Kirtland Ohio. The members of the Church had already been studying the Hebrew language, having purchased some grammars, a Hebrew Bible, and a lexicon, and had previously attempted to hire a teacher. The Hebrew scholar who came was Joshua Seixas. He spent several weeks instructing many of the members of the Church in Hebrew.[7] Why the interest in the Hebrew we might ask? Clearly it was to be able to (in the words of Pope Pius XII) 'explain the original text which, having been written by the inspired author himself, has more authority and greater weight than any even the very best translation, whether ancient or modern.'
What this shows is that not only were the early LDS aware of the challenges associated with the Bible, but that they were just as interested in going back to the original language and to the original texts (if possible) as was the rest of Christendom who were aware of these discrepancies. Despite the critics' unfounded assertions to the contrary, there has never been a leader of the LDS Church who has ever suggested that the Bible was not suitable for study and for learning the Gospel due to any shortcomings it may have.
Critics often discuss two of Nephi's statements regarding the Bible as found in the Book of Mormon. Nephi's perspective is that of modern Latter-day Saints: The Bible contains truth from God. However, it is still the work of men, and is only as reliable as the men who wrote, translated and copied it.
It is interesting that the Book of Mormon itself has begun to be seen as a witness to the textual criticism of the Bible. Source critical theory of the Old Testament splits the story of David and Goliath into two separate accounts that were later merged into the common story that we have today.[8] Scholars believe these two traditions represent an earlier source and a later source. One of the primary evidences for this argument is the fact that some of the added material is missing from the Septuagint (LXX). In a paper presented at the 2001 FAIR Conference, Benjamin McGuire presented evidence that Nephi, in borrowing from the story of David and Goliath, relied on a text that did not have the added or late material.[9] This would be in harmony with current scholarship of the Old Testament, which indicates that this material was added at the time of the captivity in Babylon, and certainly after Nephi had left Jerusalem with his Brass Plates.
Critical sources |
|
Notes
Latter-day Saints and the Bible |
|
Reliability of the Bible |
|
Creation |
|
Genesis |
|
Understanding the Bible |
|
Cultural issues |
|
The Bible and the Book of Mormon |
|
Emmanuel Tov[1], J. L. Magnes Professor of Bible at Jerusalem's Hebrew University, and editor-in-chief of the Dead Sea Scrolls publication project wrote:
The Dead Sea Scrolls also indicate that the text differed, and this was not unique to Qumran, where they were discovered:
A similar situations confronts us with the New Testament. Leon Vaganay and Christian-Bernard Amphoux[3] wrote in An Introduction to New Testament Criticism:
Christian writers often accused heretics (such as Marcion of the second century AD) of altering the Bible text. However, there is another more disturbing finding for those who insist on an inerrant Bible text:
Thus, the present-day "orthodox" Christian tradition sometimes required the original texts to be reworked to support their views or oppose the views of those with whom they disagreed. It seems strange, then, to now accuse those who do not wholly accept the "orthodox" view of "violating scripture," since that very scripture was originally tampered with by those we now label 'orthodox,' which is merely another way of saying that they won the battle to define their view as the 'proper' one.
As Bruce Metzger observed:
Odd though it may seem, scribes who thought [for themselves] were more dangerous than those who wished merely to be faithful in copying what lay before them. Many of the alterations which may be classified as intentional were no doubt introduced in good faith by copyists who believed that they were correcting an error or infelicity of language which had previously crept into the sacred text and needed to be rectified. A later scribe might even reintroduce an erroneous reading that had been previously corrected. …The manuscripts of the New Testament preserve traces of two kinds of dogmatic alterations: those which involve the elimination or alteration of what was regarded as doctrinally unacceptable or inconvenient; and those which introduce into the Scriptures ‘proof’ for a favorite theological tenet or practice....[5]
Non-LDS scholar Kenneth Clark addressed this notion.[6] Each citation has the specific page number in brackets following it.
The paper then discusses the differences between the RSV and the comparable Catholic edition, both agreed upon by the Catholic Church and the National Council of Churches:
Regarding the Long ending to Mark:
Notes
Justin Martyr, a second-century Christian author, complained that the Jews had altered scripture:
And I wish you to observe, that they [the Jews] have altogether taken away many Scriptures from the translations....[1]
Origen, a third-century Christian author, bemoaned the problem of poor textual transmission even in his era:
The differences among the manuscripts have become great, either through the negligence of some copyists or through the perverse audacity of others; they either neglect to check over what they have transcribed, or, in the process of checking, they make additions or deletions as they please.[2]
Textual scholar Bruce Metzger quoted this passage, and then observed:
Origen suggests that perhaps all of the manuscripts existing in his day may have become corrupt....[3]
The Book of Mormon describes how "plain and precious things" (1 Nephi 13꞉28) were removed from the Bible—Origen here complains of "deletions," from the scriptures, which would be the hardest changes to detect. An alteration may be detectable, but a deletion is simply gone forever.
Corinthian bishop Dionysius complained in the second century:
When my fellow-Christians invited me to write letters to them I did so. These the devil's apostles have filled with tares, taking away some things and adding others. For them the woe is reserved. Small wonder then if some have dared to tamper even with the word of the Lord himself, when they have conspired to mutilate my own humble efforts.[4]
Latter-day Saints and the Bible |
|
Reliability of the Bible |
|
Creation |
|
Genesis |
|
Understanding the Bible |
|
Cultural issues |
|
The Bible and the Book of Mormon |
|
How do Latter-day Saints regard the Holy Bible? Do they consider the Bible to be the Word of God?
Latter-day Saints consider the Bible to be holy scripture. The 8th Article of Faith states:
We believe the Bible to be the word of God as far as it is translated correctly; we also believe the Book of Mormon to be the word of God."
The proviso that the Latter-day Saints believe the Bible to be the word of God as far as it is translated correctly seems to shake some persons' confidence in The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints as a Bible-believing church. There is no reason that this should be, for it is hardly a matter of dispute that when men translate words from one language to another they can easily err, and have often done so. Simply comparing different English-language versions of the Bible should demonstrate conclusively that some people understand ancient Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek (the source languages of the Old and New Testaments) quite differently in some cases.
But let no one doubt: The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints reveres the Bible and uses it extensively in its teaching and practice. The late Elder James E. Talmage, a member of the Quorum of the Twelve, had this to say about the Bible in his classic book about the Articles of Faith:
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints accepts the Holy Bible as the foremost of her standard works, first among the books which have been proclaimed as her written guides in faith and doctrine. In the respect and sanctity with which the Latter-day Saints regard the Bible they are of like profession with Christian denominations in general, but differ from them in the additional acknowledgment of certain other scriptures as authentic and holy, which others are in harmony with the Bible, and serve to support and emphasize its facts and doctrines.
The historical and other data upon which is based the current Christian faith as to the genuineness of the Biblical record are accepted as unreservedly by the Latter-day Saints as by the members of any sect; and in literalness of interpretation this Church probably excels.
Nevertheless, the Church announces a reservation in the case of erroneous translation, which may occur as a result of human incapacity; and even in this measure of caution we are not alone, for Biblical scholars generally admit the presence of errors of the kind—both of translation and of transcription of the text. The Latter-day Saints believe the original records to be the word of God unto man, and, as far as these records have been translated correctly, the translations are regarded as equally authentic. The English Bible professes to be a translation made through the wisdom of man; in its preparation the most scholarly men have been enlisted, yet not a version has been published in which errors are not admitted. However, an impartial investigator has cause to wonder more at the paucity of errors than that mistakes are to be found at all.
There will be, there can be, no absolutely reliable translation of these or other scriptures unless it be effected through the gift of translation, as one of the endowments of the Holy Ghost. The translator must have the spirit of the prophet if he would render in another tongue the prophet's words; and human wisdom alone leads not to that possession. Let the Bible then be read reverently and with prayerful care, the reader ever seeking the light of the Spirit that he may discern between truth and the errors of men.[5]
The 8th Article of Faith states:
We believe the Bible to be the word of God as far as it is translated correctly; we also believe the Book of Mormon to be the word of God.
The proviso that the LDS believe the Bible to be the word of God as far as it is translated correctly seems to shake some persons' confidence in The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints as a Bible-believing church. There is no reason that this should be, for it is hardly a matter of dispute that when men translate words from one language to another they can easily err, and have often done so. Simply comparing different English-language versions of the Bible should demonstrate conclusively that some people understand ancient Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek (the source languages of the Old and New Testaments) quite differently in some cases.
Latter-day Saints spend 50% of their Sunday School curriculum studying the Old and New Testaments, and the other 50% studying the Book of Mormon and Doctrine and Covenants. The Bible clearly receives the majority of attention.
While not believing that the Bible—or any book—is inerrant, the Latter-day Saints are far more concerned with defending the Bible's value than in denigrating it. Harold B. Lee observed, in 1972:
I believe that the problem of our missionaries in our day too might be not so much to prove that the Book of Mormon, the Doctrine and Covenants, and the Pearl of Great Price are indeed the word of the Lord, but that the Bible, which is generally accepted as the word of God, is being doubted as having been derived from the words of inspired prophets of past generations.
In this day when the Bible is being downgraded by many who have mingled philosophies of the world with Bible scriptures to nullify their true meaning, how fortunate that our Eternal Heavenly Father, who is always concerned about the spiritual well-being of His children, has given to us a companion book of scriptures, known as the Book of Mormon, as a defense for the truths of the Bible that were written and spoken by the prophets as the Lord directed....
It is only as we forsake the traditions of men and recover faith in the Bible, the truth of which has been fully established by recent discovery and fulfillment of prophecy, that we shall once again receive that inspiration which is needed by rulers and people alike.[6]
Thomas Paine's book The Age of Reason influenced early Church leaders to criticize the Bible, and to question its translation.Author's sources:
- Thomas Paine, The Age of Reason, p.189
- The Age of Reason, p.32
Orson Pratt attacked the accuracy of the Bible.Author's sources:
- Orson Pratt's Works, "The Bible Alone An Insufficient Guide," pp.44-47
A phrase concerning baptism was later added to the Book of Mormon quotation of Isaiah 48:1, quoted in 1 Nephi 20:1.Author's sources:
- Book of Mormon, 1830 ed. p.52
- 1 Nephi 20:1"
It appears that this change was made by Joseph Smith. It is thought that this simply records a prophetic commentary on Joseph Smith's part describing the proper interpretation of the phrase "waters of Judah." It is not regarded as an error, or likely part of the original Book of Mormon plates' text.
| Original manuscript | Printer's manuscript | 1830 edition | 1840 edition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Nephi 20:1 | hea[rken & h]ear this O house of [J]acob which [are ca]lled by the name of [Israel &] are come forth out of the waters of Judah which swear by the na[me of] the Lord & make mention of the God of Israel yet they swear not in tru[t]h nor in righteousness | hearken & hear this O house of |
Hearken and hear this, O house of Jacob, which are called by the name of Israel, and are come forth out of the waters of Judah, which swear by the name of the Lord, and make mention of the God of Israel; yet they swear not in truth, nor in righteousness. | Hearken and hear this, O house of Jacob, which are called by the name of Israel, and are come forth out of the waters of Judah (or out of the waters of baptism), which swear by the name of the Lord, and make mention of the God of Israel; yet they swear not in truth, nor in righteousness. |
(The [text in brackets] in the original manuscript are missing from the physical manuscript. The strikeouts and <insertions> in the printer's manuscript are in Joseph's hand.)
The authors suggest that the Dead Sea Scrolls "present serious problems" for the Book of Mormon and the Joseph Smith "Inspired Version" of the Bible, because the "Isaiah scroll" is "proved to be word for word identical with our standard Hebrew Bible in more than 95 per cent of the text." The authors also suggest that the "Isaiah scroll" should have caused "a great deal of joy" among Mormon scholars, but did not because it is not "filled with evidence to support the text of Isaiah in the Book of Mormon."Author's sources:
- Gleason D. Archer, A Survey of Old Testament Introduction, p.19
- Courage, vol. 1, no. 1, September 1970, p.20
- Sidney B. Sperry, Progress in Archaeology, pp.52-54"
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
Latter-day Saints and the Bible |
|
Reliability of the Bible |
|
Creation |
|
Genesis |
|
Understanding the Bible |
|
Cultural issues |
|
The Bible and the Book of Mormon |
|
Video published by BYU Religious Education.
The JST is not intended primarily or solely as a restoration of lost Bible text.
As expressed in the Bible Dictionary on churchofjesuschrist.org "The JST to some extent assists in restoring the plain and precious things that have been lost from the Bible."
Two main points should be kept in mind with regards to the Joseph Smith "translation" of the Bible:
In describing the nature of the Joseph Smith Translation (JST), the leading expert, Robert J. Matthews, said:
To regard the New Translation [i.e. JST] as a product of divine inspiration given to Joseph Smith does not necessarily assume that it be a restoration of the original Bible text. It seems probable that the New Translation could be many things. For example, the nature of the work may fall into at least four categories:
- Portions may amount to restorations of content material once written by the biblical authors but since deleted from the Bible.
- Portions may consist of a record of actual historical events that were not recorded, or were recorded but never included in the biblical collection
- Portions may consist of inspired commentary by the Prophet Joseph Smith, enlarged, elaborated, and even adapted to a latter-day situation. This may be similar to what Nephi meant by "Likening" the scriptures to himself and his people in their particular circumstance. (See 1 Nephi 19:23-24; 2 Nephi 11:8).
- Some items may be a harmonization of doctrinal concepts that were revealed to the Prophet Joseph Smith independently of his translation of the Bible, but by means of which he was able to discover that a biblical passage was inaccurate.
The most fundamental question seems to be whether or not one is disposed to accept the New Translation as a divinely inspired document.[7]
The same author later observed:
It would be informative to consider various meanings of the word translate. The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) gives these definitions: "To turn from one language into another retaining the sense"; also, "To express in other words, to paraphrase." It gives another meaning as, "To interpret, explain, expound the significance of." Other dictionaries give approximately the same definitions as the OED. Although we generally think of translation as having to do with changing a word text from one language to another, that is not the only usage of the word. Translate equally means to express an idea or statement in other words, even in the same language. If people are unfamiliar with certain terminology in their own tongue, they will need an explanation. The explanation may be longer than the original, yet the original had all the meaning, either stated or implied. In common everyday discourse, when we hear something stated ambiguously or in highly technical terms, we ask the speaker to translate it for us. It is not expected that the response must come in another language, but only that the first statement be made clear. The speaker's new statement is a form of translation because it follows the basic purpose and intent of the word translation, which is to render something in understandable form…Every translation is an interpretation—a version. The translation of language cannot be a mechanical operation … Translation is a cognitive and functional process because there is not one word in every language to match with exact words in every other language. Gender, case, tense, terminology, idiom, word order, obsolete and archaic words, and shades of meaning—all make translation an interpretive process.[8]
The Joseph Smith Translation does claim to be, in part, a restoration of the original content of the Bible. This may have been done (a) by reproducing the text as it was originally written down; or, (b) it may have been about reproducing the original intent and clarifying the message of the original author of the text in question. We are not entirely sure, but in either case the JST does claim to be, in part, a restoration.
Critics who fault the JST because it doesn't match known manuscripts of the Bible are being too hasty: we do not have the original manuscripts of any text of the Bible, nor do we know the exact nature of every change made in the JST and whether a particular change was meant to be a restoration of original text.
Kent P. Jackson, another leading expert on the JST, wrote:
Some may choose to find fault with the Joseph Smith Translation because they do not see correlations between the text on ancient manuscripts. The supposition would be that if the JST revisions were justifiable, they would agree with the earliest existing manuscripts of the biblical books. This reasoning is misdirected in two ways. First, it assumes that extant ancient manuscripts accurately reproduce the original test, and both Joseph Smith and the Book of Mormon teach otherwise.[9] Because the earliest Old and New Testament manuscripts date from long after the original documents were written, we no longer have original manuscripts to compare with Joseph Smith's revisions. The second problem with faulting the JST because it does not match ancient texts is that to do so assumes that all the revisions Joseph Smith made were intended to restore original text. We have no record of him making that claim, and even in places in which the JST would restore original text it would do so not in Hebrew or Greek but in Modern English and in the scriptural idiom of early nineteenth-century America. Revisions that fit in others of the categories listed above are likewise in modern English, "given unto my servants in their weakness, after the manner of their language" (D&C 1꞉24)/[10]
The Joseph Smith Translation (JST) is not a translation in the traditional sense. Joseph did not consider himself a "translator" in the academic sense. The JST is better thought of as a kind of "inspired commentary". The Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible is not, as some members have presumed, simply a restoration of lost Biblical text or an improvement on the translation of known text. Rather, the JST also involves harmonization of doctrinal concepts, commentary and elaboration on the Biblical text, and explanations to clarify points of importance to the modern reader. As expressed in the Bible Dictionary on lds.org "The JST to some extent assists in restoring the plain and precious things that have been lost from the Bible". Joseph did not claim to be mechanically preserving some hypothetically 'perfect' Biblical text. Rather, Joseph used the extant King James text as a basis for commentary, expansion, and clarification based upon revelation, with particular attention to issues of doctrinal importance for the modern reader. Reading the JST is akin to having the prophet at your elbow as one studies—it allows Joseph to clarify, elaborate, and comment on the Biblical text in the light of modern revelation.
The JST comes from a more prophetically mature and sophisticated Joseph Smith, and provides doctrinal expansion based upon additional revelation, experience, and understanding. In general, it is probably better seen as a type of inspired commentary on the Bible text by Joseph. Its value consists not in making it the new "official" scripture, but in the insights Joseph provides readers and what Joseph himself learned during the process.
The Book of Moses was produced as a result of Joseph's efforts to clarify the Bible. This portion of the work was canonized and is part of the Pearl of Great Price. There was no attempt to canonize the rest of the JST then, or now.
Kent Jackson reports:
The original manuscripts of the JST, as well as the Bible used in the revision, still exist. They show the following process at work: Joseph Smith had his Bible in front of him, likely in his lap or on a table, and he dictated the translation to his scribes, who recorded what they heard him say. ... there are no parts of the translation in which the scribes "copied out the text of the Bible." The evidence on the manuscripts is clear that this did not happen. The Prophet dictated without punctuation and verse breaks, and those features were inserted as a separate process after the text was complete. [Some have argued that after supposedly] copying of text out of the Bible, the scribes then inserted the "numerous strikethroughs of words and phrases, interlinear insertions, and omissions," and thus Joseph Smith’s revised text was born. But the overwhelming majority of the revisions were in the original dictation and are simply part of the original writing on the manuscripts. There are indeed strikeouts and interlinear insertions on the manuscripts, but they came during a second pass through parts of the manuscripts and comprise only a minority of the revisions Joseph Smith made.[11]:20-21
In March 2017, Thomas Wayment, professor of Classics at Brigham Young University, published a paper in BYU’s Journal of Undergraduate Research titled "A Recently Recovered Source: Rethinking Joseph Smith’s Bible Translation". In a summary of their research, Wayment and his research assistant wrote:
Joseph Smith’s translation of the Bible has attracted significant attention in recent decades, drawing the interest of a wide variety of academics and those who affirm its nearly canonical status in the LDS scriptural canon. More recently, in conducting new research into the origins of Smith’s Bible translation, we uncovered evidence that Smith and his associates used a readily available Bible commentary while compiling a new Bible translation, or more properly a revision of the King James Bible. The commentary, Adam Clarke’s famous Holy Bible, Containing the Old and New Testaments, was a mainstay for Methodist theologians and biblical scholars alike, and was one of the most widely available commentaries in the mid-1820s and 1830s in America. Direct borrowing from this source has not previously been connected to Smith’s translation efforts, and the fundamental question of what Smith meant by the term "translation" with respect to his efforts to rework the biblical text can now be reconsidered in light of this new evidence. What is noteworthy in detailing the usage of this source is that Adam Clarke’s textual emendations come through Smith’s translation as inspired changes to the text. Moreover, the question of what Smith meant by the term translation should be broadened to include what now appears to have been an academic interest to update the text of the Bible. This new evidence effectively forces a reconsideration of Smith’s translation projects, particularly his Bible project, and how he used academic sources while simultaneously melding his own prophetic inspiration into the resulting text. In presenting the evidence for Smith’s usage of Clarke, our paper also addressed the larger question of what it means for Smith to have used an academic/theological Bible commentary in the process of producing a text that he subsequently defined as a translation. In doing so, we first presented the evidence for Smith’s reliance upon Adam Clarke to establish the nature of Smith’s usage of Clarke. Following that discussion, we engaged the question of how Smith approached the question of the quality of the King James Bible (hereafter KJV) translation that he was using in 1830 and what the term translation meant to both Smith and his close associates. Finally, we offered a suggestion as to how Smith came to use Clarke, as well as assessing the overall question of what these findings suggest regarding Smith as a translator and his various translation projects.
Our research has revealed that the number of direct parallels between Smith’s translation and Adam Clarke’s biblical commentary are simply too numerous and explicit to posit happenstance or coincidental overlap. The parallels between the two texts number into the hundreds, a number that is well beyond the limits of this paper to discuss. A few of them, however, demonstrate Smith’s open reliance upon Clarke and establish that he was inclined to lean on Clarke’s commentary for matters of history, textual questions, clarification of wording, and theological nuance. In presenting the evidence, we have attempted to both establish that Smith drew upon Clarke, likely at the urging of Rigdon, and we present here a broad categorization of the types of changes that Smith made when he used Clarke as a source.[12]
Wayment and Wilson-Lemmon then published a more detailed account of their findings together in Producing Ancient Scripture: Joseph Smith's Translation Projects in the Development of Mormon Christianity (2020) edited by BYU professor Michael Hubbard MacKay, Joseph Smith Papers researcher Mark Ashurst-McGee, and former BYU professor Brian M. Hauglid.[13] Wayment then published an additional article on the subject in the July 2020 issue of the Journal of Mormon History.[14]
Wayment outlined what he and Haley Wilson believed they had found:
What we found, a student assistant (Hailey Wilson Lamone) and I, we discovered that in about 200 to 300 — depending on how much change is being involved — parallels where Joseph Smith has the exact same change to a verse that Adam Clarke does. They’re verbatim. Some of them are 5 to 6 words; some of them are 2 words; some of them are a single word. But in cases where that single word is fairly unique or different, it seemed pretty obvious that he’s getting this from Adam Clarke. What really changed my worldview here is now I’m looking at what appears obvious as a text person, that the prophet has used Adam Clarke. That in the process of doing the translation, he’s either read it, has it in front of him, or he reads it at night. We started to look back through the Joseph Smith History. There’s a story of his brother-in-law presenting Joseph Smith with a copy of Adam Clarke. We do not know whose copy of Adam Clarke it is, but we do know that Nathaniel Lewis gives it to the prophet and says, "I want to use the Urim and Thummim. I want to translate some of the strange characters out of Adam Clarke’s commentary." Joseph will clearly not give him the Urim and Thummim to do that, but we know he had it in his hands. Now looking at the text, we can say that a lot of the material that happens after Genesis 24. There are no parallels to Clarke between Genesis 1–Genesis 24. But when we start to get to Matthew, it’s very clear that Adam Clarke has influenced the way he changes the Bible. It was a big moment. That article comes out in the next year. We provide appendi [sic] and documentation for some of the major changes, and we try to grapple with what this might mean.[15]
In another interview with Kurt Manwaring, Wayment addressed the charge of plagiarism directly:
When news inadvertently broke that a source had been uncovered that was used in the process of creating the JST, some were quick to use that information as a point of criticism against Joseph or against the JST. Words like "plagiarism" were quickly brought forward as a reasonable explanation of what was going on. To be clear, plagiarism is a word that to me implies an overt attempt to copy the work of another person directly and intentionally without attributing any recognition to the source from which the information was taken.
To the best of my understanding, Joseph Smith used Adam Clarke as a Bible commentary to guide his mind and thought process to consider the Bible in ways that he wouldn’t have been able to do so otherwise. It may be strong to say, but Joseph didn’t have training in ancient languages or the history of the Bible, but Adam Clarke did. And Joseph appears to have appreciated Clarke’s expertise and in using Clarke as a source, Joseph at times adopted the language of that source as he revised the Bible. I think that those who are troubled by this process are largely troubled because it contradicts a certain constructed narrative about the history of the JST and about how revelation works.
The reality of what happened is inspiring.
Joseph, who applied his own prophetic authority to the Bible in the revision process, drew upon the best available scholarship to guide his prophetic instincts. Inspiration following careful study and consideration is a prophetic model that can include many members of the church.
I hope people who read the study when it comes out will pause long enough to consider the benefit of expanding the definition of the prophetic gift to include academic study as a key component before rejecting the evidence outright.[16]
Mark Ashurst McGee of the Joseph Smith Papers team made similar points as those of Wayment at the 2020 FAIR Conference held in Provo:
In October 2020, Kent P. Jackson (Emeritus Professor of Ancient Scripture at Brigham Young University and a leading expert on the JST) responded to Wayment and Wilson-Lemmon's work.[11]
Jackson's paper identified several striking weakness to the Adam Clarke hypothesis. These include:
Jackson concluded that "none of the examples they provide can be traced to Clarke’s commentary, and almost all of them can be explained easily by other means."[11]:15
Similarly, Latter-day Saint scholar Kevin L. Barney, who has published on the JST in the past,[17] wrote that the chances for the Adam Clarke commentary influencing the production of the JST are "de minimis or negligible."[18]
To be sure, neither Jackson nor Barney are opposed to the idea that there could be secondary source influence on the production of the JST. Thus, this is a faith-neutral issue for both.
At the 2022 FAIR Conference held in Provo, UT, Professor Kent Jackson responded to the theory directly and in depth.[19]
As one LDS scholar noted:
"The Bible Dictionary in the English LDS Bible states that Joseph Smith 'continued to make modifications [in the translation] until his death in 1844.' Based on information available in the past, that was a reasonable assumption, and I taught it for many years. But we now know that it is not accurate. The best evidence points to the conclusion that when the Prophet called the translation 'finished,' he really meant it, and no changes were made in it after the summer (or possibly the fall) of 1833."[20]
Joseph did not view his revisions to the Bible as a "once and for all" or "finally completed translation" goal—he simply didn't see scripture that way. The translation could be acceptable for purposes, but still subject to later clarification or elaboration. Joseph was, however, collecting funds to publish the JST—which indicates that he believed it was ready for public use and consumption.
George Q. Cannon reported that Brigham Young heard Joseph speak about further revisions:
We have heard President Brigham Young state that the Prophet, before his death, had spoken to him about going through the translation of the scriptures again and perfecting it upon points of doctrine which the Lord had restrained him from giving in plainness and fullness at the time of which we write.[21]
We again see that the JST or any other scripture is not the ultimate source of LDS doctrine—having a living prophet is what is most vital.
The answer to this question is complex. There is no single reason; instead, there are many:
In 1978, the Church produced its new version of the KJV after years of work—it included multiple footnote and appendix entries from the JST. (Ironically, the JST was the focus of serious attention by the Church long before critics of the Church began to insist that leaders were ashamed of it.[22])
The Church magazines also launched a concerted effort to introduce Latter-day Saints to the JST material that was now easily available, and to encourage its use.[23]
Among Church leaders, Elder Bruce R. McConkie was especially vocal about the JST. In 1980, he said:
[Joseph] translated the Book of Abraham and what is called the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible. This latter is a marvelously inspired work; it is one of the great evidences of the divine mission of the Prophet. By pure revelation, he inserted many new concepts and views as, for instance, the material in the fourteenth chapter of Genesis about Melchizedek. Some chapters he rewrote and realigned so that the things said in them take on a new perspective and meaning, such as the twenty-fourth chapter of Matthew and the first chapter in the gospel of John.[24]
In 1985 Elder McConkie told members during a satellite broadcast:
As all of us should know, the Joseph Smith Translation, or Inspired Version as it is sometimes called, stands as one of the great evidences of the divine mission of the Prophet. The added truths he placed in the Bible and the corrections he made raise the resultant work to the same high status as the Book of Mormon and the Doctrine and Covenants. It is true that he did not complete the work, but it was far enough along that he intended to publish it in its present form in his lifetime.[25]
Critical sources |
|
The Book of Moses comes from the few chapters of the JST—it is essentially the JST of the first chapters of Genesis.
The translation includes many phrases from the New Testament. The following occurences of New Testament language and concepts reflected in the Book of Moses were documented by David M. Calabro—a Latter-day Saint and Curator of Eastern Christian Manuscripts at the Hill Museum and Manuscript Library at Saint John’s University.[26]
| Phrase | Location in Book of Moses | Location in New Testament |
|---|---|---|
| "Only Begotten" and "Only Begotten Son" | Moses 1:6, 13, 16, 17, 19, 21, 32, 33; 2:1, 26, 27; 3:18; 4:1, 3, 28, 5:7, 9, 57; 6:52, 57, 59, 62; 7:50, 59, 62 | John 1:14, 18; 3:16, 18; Hebrews 11:17; 1 John 4:9 |
| "transfigured before" God | Moses 1:11 | Matthew 17:2; Mark 9:2 |
| "get thee hence, Satan" | Moses 1:16 | Matthew 4:10 |
| the Holy Ghost "beareth record" of the Father and the Son | Moses 1:24; 5:9 | 1 John 5:7 |
| "by the word of my power" | Moses 1:32, 35; 2:5 | Hebrews 1:3 |
| "full of grace and truth" | Moses 1:32, 5:7 | John 1:14; cf. John 1:17 |
| "immortality and eternal life" | Moses 1:39 | Both terms are absent from the Old Testament but are relatively frequent in the New Testament: immortality occurs six times, all in Pauline epistles; eternal life occurs twenty-six times in the Gospels, Pauline epistles, epistles of John, and Jude; "eternal life" also appears elsewhere like in Moses 5:11; 6:59; 7:45. |
| "them that believe" | Moses 1:42; 4:32 | Mark 16:17; John 1:12; Romans 3:22; 4:11; 1 Corinthians 1:21; 14:22; Galatians 3:22; 2 Thessalonians 1:10; Hebrews 10:39; the contrasting phrase "them that do not believe" also appears (Rom. 15:31; 1 Cor. 10:27; 14:22) |
| "I am the Beginning and the End" | Moses 2:1 | Revelation 21:6; 22:13 |
| "Beloved Son" as a title of Christ | Moses 4:2 | Matthew 3:17; 17:5; Mark 1:11; 9:7; Luke 3:22; 9:35; 2 Peter 1:17; the phrase "beloved son" appears elsewhere in the New Testament (Luke 20:13; 1 Cor. 4:17; 2 Tim. 1:2) and in the Greek Septuagint of Gen. 22:2, but it is absent from the Hebrew and KJV Old Testament. |
| "my Chosen," as a title of Christ | Moses 4:2; 7:39 | Compare "chosen of God" in reference to Christ in Luke 23:35 and 1 Pet. 2:4 |
| "thy will be done" | Moses 4:2 | Matthew 6:10; 26:42; Luke 11:2 |
| "the glory be thine forever" | Moses 4:2 | Compare Matthew 6:13 - "For thine is the kingdom, and the power, and the glory, for ever;" note the proximity of this phrase to "thy will be done" both in Moses 4:2 and in the Lord’s prayer in Matthew 6:9–1. |
| "by the power of mine Only Begotten, I caused that [Satan] should be cast down" | Moses 4:3 | Compare Revelation 12:10 - "Now is come . . . the power of his Christ: for the accuser of our brethren is cast down"; note that the Hebrew title Satan means "accuser" |
| "the devil" | Moses 4:4 | Sixty-one instances in the New Testament, translating the Greek word diabolos |
| "carnal, sensual, and devilish" | Moses 5:13; 6:49 | James 3:15 "earthly, sensual, and devilish" |
| "Satan desireth to have thee" | Moses 5:23 | Luke 22:31 "Satan hath desired to have you" |
| "Perdition," as the title of a person | Moses 5:24 | Compare "the son of perdition" in John 17:12; 2 Thessalonians 2:3; the word perdition as an abstract noun meaning "destruction" (translating the Greek word apoleia) occurs elsewhere in the King James version of the New Testament (Philippians 1:28; 1 Timothy 6:9; Hebrews 10:39; 2 Peter 3:7; Revelation 17:8, 11) |
| "the Gospel" | Moses 5:58, 59, 8:19 | Eighty-three instances in the New Testament; the word gospel, irrespective of the English definite article, occurs 101 times in the New Testament but is not found in the Old Testament. |
| "holy angels" | Moses 5:58 | Matthew 25:31; Mark 8:38; Luke 9:26; Acts 10:22 (singular "holy angel"); Revelation 14:10 |
| "gift of the Holy Ghost" | Moses 5:58; 6:52 | Acts 2:38; 10:45 |
| "anointing" the eyes in order to see | Moses 6:35 – "anoint thine eyes with clay, and wash them, and thou shalt see" | Compare John 9:6–7, 11 (Jesus anoints the eyes of a blind man with clay and commands him to wash in the pool of Siloam, and he "came seeing"); Revelation 3:18 (the Lord tells the church in Laodicea, "anoint thine eyes with eyesalve, that thou mayest see"); these are the only passages in the Bible that refer to anointing the eyes |
| "no man laid hands on him" | Moses 6:39 | John 7:30, 44; 8:20 |
| "my God, and your God" | Moses 6:43 | John 20:17 |
| "only name under heaven whereby salvation shall come" | Moses 6:52 | Acts 4:12 |
| collocation of water, blood, and Spirit | Moses 6:59-60 | 1 John 5:6, 8 |
| "born again of water and the Spirit"; "born of the Spirit"; "born again"; "born of water and of the Spirit"; "born of the Spirit" | Moses 6:59, 65 | John 3:3, 5-8 |
| "the mysteries of the kingdom of heaven" | Moses 6:59 | Matthew 13:11. The phrase "kingdom of heaven" is absent from the Old Testament; in the New Testament it is found only in Matthew (thirty-two occurrences), but it is frequent in rabbinic literature |
| "cleansed by blood, even the blood of mine Only Begotten" | Moses 6:59 | Compare 1 John 1:7 ("the blood of Jesus Christ his Son cleanseth us from all sin") |
| "the words of eternal life" | Moses 6:59 | John 6:68 |
| eternal life "in the world to come" | Moses 6:59 | Mark 10:30; Luke 18:30; the phrase "the world to come" is absent from the Old Testament but occurs five times in the New Testament; other than the two just quoted, see Matthew 12:32; Hebrews 2:5; 6:5 |
| "by the Spirit ye are justified" | Moses 6:60 | Compare 1 Corinthians 6:11; 1 Timothy 3:16 |
| "the Comforter," referring to the Holy Ghost | Moses 6:61 | John 14:16, 26; 15:26; 16:7 |
| "the inner man" | Moses 6:65 | Ephesians 3:16; Romans 7:22; 2 Corinthians 4:16 |
| "baptized with fire and with the Holy Ghost" | Moses 6:66 | Matthew 3:11; Luke 3:16 |
| "they were of one heart and one mind" | Moses 7:18 | Compare Acts 4:32 |
| "in the bosom of the Father," referring to heaven | Moses 7:24, 47 | John 1:18 (note that JST deletes this phrase in this verse, perhaps implying that it entered the text sometime after its original composition) |
| "a great chain in his hand" | Moses 7:26 | Revelation 20:1 (here the one holding the chain is an angel, unlike Moses 7:26, in which it is the devil) |
| commandment to "love one another" | Moses 7:33 | John 13:34, 35; 15:12, 17; Romans 12:10; 13:8; 1 Thessalonians 3:12; 4:9; 1 Peter 1:22; 1 John 3:11, 23; 4:7, 11, 12; 2 John 1:5 |
| "without affection" | Moses 7:33 | Romans 1:31; 2 Timothy 3:3 |
| "the Lamb is slain from the foundation of the world" | Moses 7:47 | Compare Revelation 13:8 – "the Lamb slain from the foundation of the world," as a noun phrase); the term "the Lamb" is used as a title of the Messiah only in the New Testament and is distinctively Johannine (John 1:29, 36; twenty-seven instances in Revelation), and the words lamb and slain collocate only in Revelation 5:6, 12; 13:8. |
| "climb up" by a gate or door, as a metaphor of progression through Christ | Moses 7:53 | John 10:1 |
Video by The Interpreter Foundation.
This language can be explained by a few possible factors, not all mutually exclusive.
The first possibility to consider is that Joseph Smith translated the Book of Moses into a vernacular that was comprehensible to his 19th century audience. Joseph's contemporaries were steeped in biblical language and used it even in everyday speech. The language of the New Testament was the natural way to discuss certain theological ideas.
D&C 1꞉24 tells us that in revelation, God uses the language of his audience to communicate effectively" Behold, I am God and have spoken it; these commandments are of me, and were given unto my servants in their weakness, after the manner of their language, that they might come to understanding."[27]
Another possibility is that the Book of Moses was originally written in an early Christian context. That would place the composition of the Book of Moses in the 1st and 2nd century AD (about 1900 to 1800 years ago). Calabro outlined and defended this theory.[26] Calabro argues that the Book of Moses can still preserve actual events from the life of Moses while placing the story in a Christian context describing it with Christian language. Thus, Joseph Smith could actually be restoring lost understanding of Moses—but that information has already been filtered through New Testament language.
One potential weakness of this theory is that it disrupts the understanding of many Church members about the Book of Moses, since it has more traditionally been seen as a restoration of Moses' writings in Genesis. However, Joseph Smith does not seem to have left a detailed account of what the Book of Moses represents. Joseph saw the JST as a restoration of "many important points touching the salvation of men, [that] had been taken from the Bible, or lost before it was compiled."[28]
This theory could also, in essence, be turned on its head, making an ancient version of the Book of Moses the source of subsequent Christian writing. Latter-day Saint author Jeff Lindsay and former BYU professor Noel Reynolds have theorized that the Book of Moses influenced the language of the Book of Mormon via the brass plates or another source.[29]
Speaking in reference to the Bible, the Book of Mormon has God announce that "I speak the same words unto one nation like unto another. And when the two enations shall run together the testimony of the two nations shall run together also."[30]
It is certainly possible that the same concepts were revealed to Moses with similar language as that used in the New Testament.
There are therefore multiple models which would explain the similarity between the Book of Moses and the New Testament. Given that the Book of Moses claims to be a translation, it is hardly strange that it would echo another translation (the KJV bible) that discusses the same ideas and issues.
The scriptures affirm that there is "One God" consisting of Father, Son, and Holy Ghost. A great debate in Christian history has been the nature of this oneness.
Protestant critics do not like the fact that Latter-day Saints reject the nonbiblical Nicene Creed, which teaches a oneness of substance. Latter-day Saints believe that God is one, but accept the Biblical witness that this is a oneness of purpose, intent, mind, will, and love, into which believers are invited to participate (see John 17꞉22-23). Thus, it is proper to speak of "God" in a singular sense, but Latter-day Saints also recognize that there is more than one divine person—for example, the Father and the Son.
This is not a contradiction; it merely demonstrates that the Latter-day Saints do not accept Nicene trinitarianism.
When God gives new insight and revelation, he doesn't typically "rewrite" all scripture that has gone before: He simply adds to it.
The creation account in the Book of Abraham supports a plurality of gods. Critics claim that the Bible does not support this. However, there are two errors in the assumption that the Bible does not support a plurality of gods.
Error #1: It is debatable that the unedited King James Version of Genesis truly only includes "one God." There are clearly multiple divine personages in Genesis:
And the LORD God said, Behold, the man is become as one of us, to know good and evil.... (Genesis 3꞉22)
Only creeds or convictions that insist on a single divine being make us unable to notice.
Error #2: The Joseph Smith Translation of Genesis actually did clarify the role and existence of multiple divine personages. The Book of Moses in the Pearl of Great Price (which is the simply the Joseph Smith Translation of Genesis) has many examples of multiple divine personages:
I have a work for thee, Moses, my son; and thou art in the similitude of mine Only Begotten; and mine Only Begotten is and shall be the Savior, for he is full of grace and truth; but there is no God beside me, and all things are present with me, for I know them all (Moses 1꞉6).
Moses looked upon Satan and said: Who art thou? For behold, I am a son of God, in the similitude of his Only Begotten; and where is thy glory, that I should worship thee? (Moses 1꞉13)
for God said unto me: Thou art after the similitude of mine Only Begotten....Call upon God in the name of mine Only Begotten, and worship me. (Moses 1꞉16-17)
Moses lifted up his eyes unto heaven, being filled with the Holy Ghost, which beareth record of the Father and the Son; (Moses 1꞉24)
And worlds without number have I created; and I also created them for mine own purpose; and by the Son I created them, which is mine Only Begotten. (Moses 1꞉33)
That's just the first chapter of the JST of Genesis. There are many, many more examples in Moses.
In chapter 2 of Moses, God prefaces his remarks by saying, "I am the Beginning and the End, the Almighty God; by mine Only Begotten I created these things; yea, in the beginning I created the heaven, and the earth upon which thou standest" (Moses 2꞉1).
So, in each case when "I, God" did something in the creation, it should be understood that the Only Begotten is also involved, since it is by him that God created all. So, there are multiple divine personages in each mention in the verses that follow.
Some critics have claimed that the Church is "embarrassed" by the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible. [31]
This claim is contradicted by an enormous amount of historical evidence. The claim was made in 1977. In 1978, the Church produced its new version of the KJV after years of work. Thus, the JST was the focus of serious attention by the Church long before the Tanners began to insist that leaders were ashamed of it.[32] It had multiple footnote and appendix entries from the JST.
The Church magazines also launched a concerted effort to introduce Latter-day Saints to the JST material that was now easily available, and to encourage its use. Some examples of this effort published around the time the Tanners were making their claim include:
The Church is not, and was not, embarrassed by the JST. In its historical context, the critics' claim is incredibly ill-informed.
Critical sources |
|
Parallel passages from the Book of Mormon and Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible sometimes disagree not only with the King James Version of the Bible, but also with each other. Critics ask why Joseph's earlier work (i.e., the Book of Mormon) generally followed the King James Version of the Bible closely while his later work (i.e., the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible) did not. Critics ask which translation did Joseph get right, implying that one is wrong, hence bringing his prophetic calling into question. Critics generally cite any of a number of passages from Matthew 5-7 from the King James Version and Joseph Smith Translation and 3 Nephi 12-14 from the Book of Mormon. A much celebrated example is:
Matthew 6:25-27 (King James Version)
3 Nephi 13꞉25-27) (Book of Mormon)
Matthew 6:25-27 (Joseph Smith Translation)
Joseph had different purposes in mind in his different translations. This is not unique or unusual in scripture—even the Bible. Hence, neither the Book of Mormon nor the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible can be discounted because of seeming discrepancies with each other or with the King James Version of the Bible.
Joseph Smith had different purposes in mind when bringing forth the Book of Mormon and the Joseph smith Translation. His purpose in bringing forth the Book of Mormon was to witness "the reality that "Jesus is the Christ, the Eternal God, manifesting himself unto all nations". Departing from the King James Version, i.e., the translation familiar to those who would become the Book of Mormon's first readers, would have been a stumbling block in achieving its purpose. On the other hand, Joseph's later purpose in bringing forth the Joseph Smith Translation is largely understood to have been one of redaction, or inspired commentary—to resolve confusion regarding biblical interpretation[33] Hence the different wording, and in some cases, even content.
Gleason Archer, well known Evangelical Christian and the Author of a highly respected book called "Encyclopedia of Bible Difficulties", addresses the issue of Paul citing deficient Greek Septuagint translations that appear in our New Testaments today in lieu of better translations of the Old Testament he could have come up with. Archer says:
Suppose Paul had chosen to work out a new, more accurate translation into Greek directly from Hebrew. Might not the Bereans have said in reply, "that’s not the way we find it in our Bible. How do we know you have not slanted your different rendering here and there in order to favor you new teaching about Christ?" In order to avoid suspicion and misunderstanding, it was imperative for the apostles and evangelists to stick with the Septuagint in their preaching and teaching, both oral and written.
We, like the first-century apostles, resort to these standard translations to teach our people in terms they can verify by resorting to their own Bibles, yet admittedly, none of these translations is completely free of faults. We use them nevertheless, for the purpose of more effective communication than if we were to translate directly from the Hebrew or Greek.[34]
Archer's point is that it is more important in certain settings that Paul's writings be familiar rather than 100% precise.
Key sources |
|
FAIR links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
Video published by BYU Religious Education.
|
Print |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Notes
LDS leaders claimed that "Catholics conspired to alter the Bible," but this is proven wrong by the Dead Sea Scrolls.Author's sources:
- 1 Nephi 13:26-29
- Joseph Fielding Smith, Jr., Religious Truths Defined, p.175
- Mark E. Peterson, As Translated Correctly, p.4, 14
- The Evening and the Morning Star (vol. 1, No. 1, p.3)
The "Inspired Version" of the Bible has been a "source of much embarrassment" for leaders of the Church.Author's sources:
- Brigham Young, Journal of Discourses 3:116.
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
Latter-day Saints and the Bible |
|
Reliability of the Bible |
|
Creation |
|
Genesis |
|
Understanding the Bible |
|
Cultural issues |
|
The Bible and the Book of Mormon |
|
Video published by BYU Religious Education.
The JST is not intended primarily or solely as a restoration of lost Bible text.
As expressed in the Bible Dictionary on churchofjesuschrist.org "The JST to some extent assists in restoring the plain and precious things that have been lost from the Bible."
Two main points should be kept in mind with regards to the Joseph Smith "translation" of the Bible:
In describing the nature of the Joseph Smith Translation (JST), the leading expert, Robert J. Matthews, said:
To regard the New Translation [i.e. JST] as a product of divine inspiration given to Joseph Smith does not necessarily assume that it be a restoration of the original Bible text. It seems probable that the New Translation could be many things. For example, the nature of the work may fall into at least four categories:
- Portions may amount to restorations of content material once written by the biblical authors but since deleted from the Bible.
- Portions may consist of a record of actual historical events that were not recorded, or were recorded but never included in the biblical collection
- Portions may consist of inspired commentary by the Prophet Joseph Smith, enlarged, elaborated, and even adapted to a latter-day situation. This may be similar to what Nephi meant by "Likening" the scriptures to himself and his people in their particular circumstance. (See 1 Nephi 19:23-24; 2 Nephi 11:8).
- Some items may be a harmonization of doctrinal concepts that were revealed to the Prophet Joseph Smith independently of his translation of the Bible, but by means of which he was able to discover that a biblical passage was inaccurate.
The most fundamental question seems to be whether or not one is disposed to accept the New Translation as a divinely inspired document.[1]
The same author later observed:
It would be informative to consider various meanings of the word translate. The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) gives these definitions: "To turn from one language into another retaining the sense"; also, "To express in other words, to paraphrase." It gives another meaning as, "To interpret, explain, expound the significance of." Other dictionaries give approximately the same definitions as the OED. Although we generally think of translation as having to do with changing a word text from one language to another, that is not the only usage of the word. Translate equally means to express an idea or statement in other words, even in the same language. If people are unfamiliar with certain terminology in their own tongue, they will need an explanation. The explanation may be longer than the original, yet the original had all the meaning, either stated or implied. In common everyday discourse, when we hear something stated ambiguously or in highly technical terms, we ask the speaker to translate it for us. It is not expected that the response must come in another language, but only that the first statement be made clear. The speaker's new statement is a form of translation because it follows the basic purpose and intent of the word translation, which is to render something in understandable form…Every translation is an interpretation—a version. The translation of language cannot be a mechanical operation … Translation is a cognitive and functional process because there is not one word in every language to match with exact words in every other language. Gender, case, tense, terminology, idiom, word order, obsolete and archaic words, and shades of meaning—all make translation an interpretive process.[2]
The Joseph Smith Translation does claim to be, in part, a restoration of the original content of the Bible. This may have been done (a) by reproducing the text as it was originally written down; or, (b) it may have been about reproducing the original intent and clarifying the message of the original author of the text in question. We are not entirely sure, but in either case the JST does claim to be, in part, a restoration.
Critics who fault the JST because it doesn't match known manuscripts of the Bible are being too hasty: we do not have the original manuscripts of any text of the Bible, nor do we know the exact nature of every change made in the JST and whether a particular change was meant to be a restoration of original text.
Kent P. Jackson, another leading expert on the JST, wrote:
Some may choose to find fault with the Joseph Smith Translation because they do not see correlations between the text on ancient manuscripts. The supposition would be that if the JST revisions were justifiable, they would agree with the earliest existing manuscripts of the biblical books. This reasoning is misdirected in two ways. First, it assumes that extant ancient manuscripts accurately reproduce the original test, and both Joseph Smith and the Book of Mormon teach otherwise.[3] Because the earliest Old and New Testament manuscripts date from long after the original documents were written, we no longer have original manuscripts to compare with Joseph Smith's revisions. The second problem with faulting the JST because it does not match ancient texts is that to do so assumes that all the revisions Joseph Smith made were intended to restore original text. We have no record of him making that claim, and even in places in which the JST would restore original text it would do so not in Hebrew or Greek but in Modern English and in the scriptural idiom of early nineteenth-century America. Revisions that fit in others of the categories listed above are likewise in modern English, "given unto my servants in their weakness, after the manner of their language" (D&C 1꞉24)/[4]
The Joseph Smith Translation (JST) is not a translation in the traditional sense. Joseph did not consider himself a "translator" in the academic sense. The JST is better thought of as a kind of "inspired commentary". The Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible is not, as some members have presumed, simply a restoration of lost Biblical text or an improvement on the translation of known text. Rather, the JST also involves harmonization of doctrinal concepts, commentary and elaboration on the Biblical text, and explanations to clarify points of importance to the modern reader. As expressed in the Bible Dictionary on lds.org "The JST to some extent assists in restoring the plain and precious things that have been lost from the Bible". Joseph did not claim to be mechanically preserving some hypothetically 'perfect' Biblical text. Rather, Joseph used the extant King James text as a basis for commentary, expansion, and clarification based upon revelation, with particular attention to issues of doctrinal importance for the modern reader. Reading the JST is akin to having the prophet at your elbow as one studies—it allows Joseph to clarify, elaborate, and comment on the Biblical text in the light of modern revelation.
The JST comes from a more prophetically mature and sophisticated Joseph Smith, and provides doctrinal expansion based upon additional revelation, experience, and understanding. In general, it is probably better seen as a type of inspired commentary on the Bible text by Joseph. Its value consists not in making it the new "official" scripture, but in the insights Joseph provides readers and what Joseph himself learned during the process.
The Book of Moses was produced as a result of Joseph's efforts to clarify the Bible. This portion of the work was canonized and is part of the Pearl of Great Price. There was no attempt to canonize the rest of the JST then, or now.
Kent Jackson reports:
The original manuscripts of the JST, as well as the Bible used in the revision, still exist. They show the following process at work: Joseph Smith had his Bible in front of him, likely in his lap or on a table, and he dictated the translation to his scribes, who recorded what they heard him say. ... there are no parts of the translation in which the scribes "copied out the text of the Bible." The evidence on the manuscripts is clear that this did not happen. The Prophet dictated without punctuation and verse breaks, and those features were inserted as a separate process after the text was complete. [Some have argued that after supposedly] copying of text out of the Bible, the scribes then inserted the "numerous strikethroughs of words and phrases, interlinear insertions, and omissions," and thus Joseph Smith’s revised text was born. But the overwhelming majority of the revisions were in the original dictation and are simply part of the original writing on the manuscripts. There are indeed strikeouts and interlinear insertions on the manuscripts, but they came during a second pass through parts of the manuscripts and comprise only a minority of the revisions Joseph Smith made.[5]:20-21
In March 2017, Thomas Wayment, professor of Classics at Brigham Young University, published a paper in BYU’s Journal of Undergraduate Research titled "A Recently Recovered Source: Rethinking Joseph Smith’s Bible Translation". In a summary of their research, Wayment and his research assistant wrote:
Joseph Smith’s translation of the Bible has attracted significant attention in recent decades, drawing the interest of a wide variety of academics and those who affirm its nearly canonical status in the LDS scriptural canon. More recently, in conducting new research into the origins of Smith’s Bible translation, we uncovered evidence that Smith and his associates used a readily available Bible commentary while compiling a new Bible translation, or more properly a revision of the King James Bible. The commentary, Adam Clarke’s famous Holy Bible, Containing the Old and New Testaments, was a mainstay for Methodist theologians and biblical scholars alike, and was one of the most widely available commentaries in the mid-1820s and 1830s in America. Direct borrowing from this source has not previously been connected to Smith’s translation efforts, and the fundamental question of what Smith meant by the term "translation" with respect to his efforts to rework the biblical text can now be reconsidered in light of this new evidence. What is noteworthy in detailing the usage of this source is that Adam Clarke’s textual emendations come through Smith’s translation as inspired changes to the text. Moreover, the question of what Smith meant by the term translation should be broadened to include what now appears to have been an academic interest to update the text of the Bible. This new evidence effectively forces a reconsideration of Smith’s translation projects, particularly his Bible project, and how he used academic sources while simultaneously melding his own prophetic inspiration into the resulting text. In presenting the evidence for Smith’s usage of Clarke, our paper also addressed the larger question of what it means for Smith to have used an academic/theological Bible commentary in the process of producing a text that he subsequently defined as a translation. In doing so, we first presented the evidence for Smith’s reliance upon Adam Clarke to establish the nature of Smith’s usage of Clarke. Following that discussion, we engaged the question of how Smith approached the question of the quality of the King James Bible (hereafter KJV) translation that he was using in 1830 and what the term translation meant to both Smith and his close associates. Finally, we offered a suggestion as to how Smith came to use Clarke, as well as assessing the overall question of what these findings suggest regarding Smith as a translator and his various translation projects.
Our research has revealed that the number of direct parallels between Smith’s translation and Adam Clarke’s biblical commentary are simply too numerous and explicit to posit happenstance or coincidental overlap. The parallels between the two texts number into the hundreds, a number that is well beyond the limits of this paper to discuss. A few of them, however, demonstrate Smith’s open reliance upon Clarke and establish that he was inclined to lean on Clarke’s commentary for matters of history, textual questions, clarification of wording, and theological nuance. In presenting the evidence, we have attempted to both establish that Smith drew upon Clarke, likely at the urging of Rigdon, and we present here a broad categorization of the types of changes that Smith made when he used Clarke as a source.[6]
Wayment and Wilson-Lemmon then published a more detailed account of their findings together in Producing Ancient Scripture: Joseph Smith's Translation Projects in the Development of Mormon Christianity (2020) edited by BYU professor Michael Hubbard MacKay, Joseph Smith Papers researcher Mark Ashurst-McGee, and former BYU professor Brian M. Hauglid.[7] Wayment then published an additional article on the subject in the July 2020 issue of the Journal of Mormon History.[8]
Wayment outlined what he and Haley Wilson believed they had found:
What we found, a student assistant (Hailey Wilson Lamone) and I, we discovered that in about 200 to 300 — depending on how much change is being involved — parallels where Joseph Smith has the exact same change to a verse that Adam Clarke does. They’re verbatim. Some of them are 5 to 6 words; some of them are 2 words; some of them are a single word. But in cases where that single word is fairly unique or different, it seemed pretty obvious that he’s getting this from Adam Clarke. What really changed my worldview here is now I’m looking at what appears obvious as a text person, that the prophet has used Adam Clarke. That in the process of doing the translation, he’s either read it, has it in front of him, or he reads it at night. We started to look back through the Joseph Smith History. There’s a story of his brother-in-law presenting Joseph Smith with a copy of Adam Clarke. We do not know whose copy of Adam Clarke it is, but we do know that Nathaniel Lewis gives it to the prophet and says, "I want to use the Urim and Thummim. I want to translate some of the strange characters out of Adam Clarke’s commentary." Joseph will clearly not give him the Urim and Thummim to do that, but we know he had it in his hands. Now looking at the text, we can say that a lot of the material that happens after Genesis 24. There are no parallels to Clarke between Genesis 1–Genesis 24. But when we start to get to Matthew, it’s very clear that Adam Clarke has influenced the way he changes the Bible. It was a big moment. That article comes out in the next year. We provide appendi [sic] and documentation for some of the major changes, and we try to grapple with what this might mean.[9]
In another interview with Kurt Manwaring, Wayment addressed the charge of plagiarism directly:
When news inadvertently broke that a source had been uncovered that was used in the process of creating the JST, some were quick to use that information as a point of criticism against Joseph or against the JST. Words like "plagiarism" were quickly brought forward as a reasonable explanation of what was going on. To be clear, plagiarism is a word that to me implies an overt attempt to copy the work of another person directly and intentionally without attributing any recognition to the source from which the information was taken.
To the best of my understanding, Joseph Smith used Adam Clarke as a Bible commentary to guide his mind and thought process to consider the Bible in ways that he wouldn’t have been able to do so otherwise. It may be strong to say, but Joseph didn’t have training in ancient languages or the history of the Bible, but Adam Clarke did. And Joseph appears to have appreciated Clarke’s expertise and in using Clarke as a source, Joseph at times adopted the language of that source as he revised the Bible. I think that those who are troubled by this process are largely troubled because it contradicts a certain constructed narrative about the history of the JST and about how revelation works.
The reality of what happened is inspiring.
Joseph, who applied his own prophetic authority to the Bible in the revision process, drew upon the best available scholarship to guide his prophetic instincts. Inspiration following careful study and consideration is a prophetic model that can include many members of the church.
I hope people who read the study when it comes out will pause long enough to consider the benefit of expanding the definition of the prophetic gift to include academic study as a key component before rejecting the evidence outright.[10]
Mark Ashurst McGee of the Joseph Smith Papers team made similar points as those of Wayment at the 2020 FAIR Conference held in Provo:
In October 2020, Kent P. Jackson (Emeritus Professor of Ancient Scripture at Brigham Young University and a leading expert on the JST) responded to Wayment and Wilson-Lemmon's work.[5]
Jackson's paper identified several striking weakness to the Adam Clarke hypothesis. These include:
Jackson concluded that "none of the examples they provide can be traced to Clarke’s commentary, and almost all of them can be explained easily by other means."[5]:15
Similarly, Latter-day Saint scholar Kevin L. Barney, who has published on the JST in the past,[11] wrote that the chances for the Adam Clarke commentary influencing the production of the JST are "de minimis or negligible."[12]
To be sure, neither Jackson nor Barney are opposed to the idea that there could be secondary source influence on the production of the JST. Thus, this is a faith-neutral issue for both.
At the 2022 FAIR Conference held in Provo, UT, Professor Kent Jackson responded to the theory directly and in depth.[13]
As one LDS scholar noted:
"The Bible Dictionary in the English LDS Bible states that Joseph Smith 'continued to make modifications [in the translation] until his death in 1844.' Based on information available in the past, that was a reasonable assumption, and I taught it for many years. But we now know that it is not accurate. The best evidence points to the conclusion that when the Prophet called the translation 'finished,' he really meant it, and no changes were made in it after the summer (or possibly the fall) of 1833."[14]
Joseph did not view his revisions to the Bible as a "once and for all" or "finally completed translation" goal—he simply didn't see scripture that way. The translation could be acceptable for purposes, but still subject to later clarification or elaboration. Joseph was, however, collecting funds to publish the JST—which indicates that he believed it was ready for public use and consumption.
George Q. Cannon reported that Brigham Young heard Joseph speak about further revisions:
We have heard President Brigham Young state that the Prophet, before his death, had spoken to him about going through the translation of the scriptures again and perfecting it upon points of doctrine which the Lord had restrained him from giving in plainness and fullness at the time of which we write.[15]
We again see that the JST or any other scripture is not the ultimate source of LDS doctrine—having a living prophet is what is most vital.
The answer to this question is complex. There is no single reason; instead, there are many:
In 1978, the Church produced its new version of the KJV after years of work—it included multiple footnote and appendix entries from the JST. (Ironically, the JST was the focus of serious attention by the Church long before critics of the Church began to insist that leaders were ashamed of it.[16])
The Church magazines also launched a concerted effort to introduce Latter-day Saints to the JST material that was now easily available, and to encourage its use.[17]
Among Church leaders, Elder Bruce R. McConkie was especially vocal about the JST. In 1980, he said:
[Joseph] translated the Book of Abraham and what is called the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible. This latter is a marvelously inspired work; it is one of the great evidences of the divine mission of the Prophet. By pure revelation, he inserted many new concepts and views as, for instance, the material in the fourteenth chapter of Genesis about Melchizedek. Some chapters he rewrote and realigned so that the things said in them take on a new perspective and meaning, such as the twenty-fourth chapter of Matthew and the first chapter in the gospel of John.[18]
In 1985 Elder McConkie told members during a satellite broadcast:
As all of us should know, the Joseph Smith Translation, or Inspired Version as it is sometimes called, stands as one of the great evidences of the divine mission of the Prophet. The added truths he placed in the Bible and the corrections he made raise the resultant work to the same high status as the Book of Mormon and the Doctrine and Covenants. It is true that he did not complete the work, but it was far enough along that he intended to publish it in its present form in his lifetime.[19]
Critical sources |
|
The Book of Moses comes from the few chapters of the JST—it is essentially the JST of the first chapters of Genesis.
The translation includes many phrases from the New Testament. The following occurences of New Testament language and concepts reflected in the Book of Moses were documented by David M. Calabro—a Latter-day Saint and Curator of Eastern Christian Manuscripts at the Hill Museum and Manuscript Library at Saint John’s University.[20]
| Phrase | Location in Book of Moses | Location in New Testament |
|---|---|---|
| "Only Begotten" and "Only Begotten Son" | Moses 1:6, 13, 16, 17, 19, 21, 32, 33; 2:1, 26, 27; 3:18; 4:1, 3, 28, 5:7, 9, 57; 6:52, 57, 59, 62; 7:50, 59, 62 | John 1:14, 18; 3:16, 18; Hebrews 11:17; 1 John 4:9 |
| "transfigured before" God | Moses 1:11 | Matthew 17:2; Mark 9:2 |
| "get thee hence, Satan" | Moses 1:16 | Matthew 4:10 |
| the Holy Ghost "beareth record" of the Father and the Son | Moses 1:24; 5:9 | 1 John 5:7 |
| "by the word of my power" | Moses 1:32, 35; 2:5 | Hebrews 1:3 |
| "full of grace and truth" | Moses 1:32, 5:7 | John 1:14; cf. John 1:17 |
| "immortality and eternal life" | Moses 1:39 | Both terms are absent from the Old Testament but are relatively frequent in the New Testament: immortality occurs six times, all in Pauline epistles; eternal life occurs twenty-six times in the Gospels, Pauline epistles, epistles of John, and Jude; "eternal life" also appears elsewhere like in Moses 5:11; 6:59; 7:45. |
| "them that believe" | Moses 1:42; 4:32 | Mark 16:17; John 1:12; Romans 3:22; 4:11; 1 Corinthians 1:21; 14:22; Galatians 3:22; 2 Thessalonians 1:10; Hebrews 10:39; the contrasting phrase "them that do not believe" also appears (Rom. 15:31; 1 Cor. 10:27; 14:22) |
| "I am the Beginning and the End" | Moses 2:1 | Revelation 21:6; 22:13 |
| "Beloved Son" as a title of Christ | Moses 4:2 | Matthew 3:17; 17:5; Mark 1:11; 9:7; Luke 3:22; 9:35; 2 Peter 1:17; the phrase "beloved son" appears elsewhere in the New Testament (Luke 20:13; 1 Cor. 4:17; 2 Tim. 1:2) and in the Greek Septuagint of Gen. 22:2, but it is absent from the Hebrew and KJV Old Testament. |
| "my Chosen," as a title of Christ | Moses 4:2; 7:39 | Compare "chosen of God" in reference to Christ in Luke 23:35 and 1 Pet. 2:4 |
| "thy will be done" | Moses 4:2 | Matthew 6:10; 26:42; Luke 11:2 |
| "the glory be thine forever" | Moses 4:2 | Compare Matthew 6:13 - "For thine is the kingdom, and the power, and the glory, for ever;" note the proximity of this phrase to "thy will be done" both in Moses 4:2 and in the Lord’s prayer in Matthew 6:9–1. |
| "by the power of mine Only Begotten, I caused that [Satan] should be cast down" | Moses 4:3 | Compare Revelation 12:10 - "Now is come . . . the power of his Christ: for the accuser of our brethren is cast down"; note that the Hebrew title Satan means "accuser" |
| "the devil" | Moses 4:4 | Sixty-one instances in the New Testament, translating the Greek word diabolos |
| "carnal, sensual, and devilish" | Moses 5:13; 6:49 | James 3:15 "earthly, sensual, and devilish" |
| "Satan desireth to have thee" | Moses 5:23 | Luke 22:31 "Satan hath desired to have you" |
| "Perdition," as the title of a person | Moses 5:24 | Compare "the son of perdition" in John 17:12; 2 Thessalonians 2:3; the word perdition as an abstract noun meaning "destruction" (translating the Greek word apoleia) occurs elsewhere in the King James version of the New Testament (Philippians 1:28; 1 Timothy 6:9; Hebrews 10:39; 2 Peter 3:7; Revelation 17:8, 11) |
| "the Gospel" | Moses 5:58, 59, 8:19 | Eighty-three instances in the New Testament; the word gospel, irrespective of the English definite article, occurs 101 times in the New Testament but is not found in the Old Testament. |
| "holy angels" | Moses 5:58 | Matthew 25:31; Mark 8:38; Luke 9:26; Acts 10:22 (singular "holy angel"); Revelation 14:10 |
| "gift of the Holy Ghost" | Moses 5:58; 6:52 | Acts 2:38; 10:45 |
| "anointing" the eyes in order to see | Moses 6:35 – "anoint thine eyes with clay, and wash them, and thou shalt see" | Compare John 9:6–7, 11 (Jesus anoints the eyes of a blind man with clay and commands him to wash in the pool of Siloam, and he "came seeing"); Revelation 3:18 (the Lord tells the church in Laodicea, "anoint thine eyes with eyesalve, that thou mayest see"); these are the only passages in the Bible that refer to anointing the eyes |
| "no man laid hands on him" | Moses 6:39 | John 7:30, 44; 8:20 |
| "my God, and your God" | Moses 6:43 | John 20:17 |
| "only name under heaven whereby salvation shall come" | Moses 6:52 | Acts 4:12 |
| collocation of water, blood, and Spirit | Moses 6:59-60 | 1 John 5:6, 8 |
| "born again of water and the Spirit"; "born of the Spirit"; "born again"; "born of water and of the Spirit"; "born of the Spirit" | Moses 6:59, 65 | John 3:3, 5-8 |
| "the mysteries of the kingdom of heaven" | Moses 6:59 | Matthew 13:11. The phrase "kingdom of heaven" is absent from the Old Testament; in the New Testament it is found only in Matthew (thirty-two occurrences), but it is frequent in rabbinic literature |
| "cleansed by blood, even the blood of mine Only Begotten" | Moses 6:59 | Compare 1 John 1:7 ("the blood of Jesus Christ his Son cleanseth us from all sin") |
| "the words of eternal life" | Moses 6:59 | John 6:68 |
| eternal life "in the world to come" | Moses 6:59 | Mark 10:30; Luke 18:30; the phrase "the world to come" is absent from the Old Testament but occurs five times in the New Testament; other than the two just quoted, see Matthew 12:32; Hebrews 2:5; 6:5 |
| "by the Spirit ye are justified" | Moses 6:60 | Compare 1 Corinthians 6:11; 1 Timothy 3:16 |
| "the Comforter," referring to the Holy Ghost | Moses 6:61 | John 14:16, 26; 15:26; 16:7 |
| "the inner man" | Moses 6:65 | Ephesians 3:16; Romans 7:22; 2 Corinthians 4:16 |
| "baptized with fire and with the Holy Ghost" | Moses 6:66 | Matthew 3:11; Luke 3:16 |
| "they were of one heart and one mind" | Moses 7:18 | Compare Acts 4:32 |
| "in the bosom of the Father," referring to heaven | Moses 7:24, 47 | John 1:18 (note that JST deletes this phrase in this verse, perhaps implying that it entered the text sometime after its original composition) |
| "a great chain in his hand" | Moses 7:26 | Revelation 20:1 (here the one holding the chain is an angel, unlike Moses 7:26, in which it is the devil) |
| commandment to "love one another" | Moses 7:33 | John 13:34, 35; 15:12, 17; Romans 12:10; 13:8; 1 Thessalonians 3:12; 4:9; 1 Peter 1:22; 1 John 3:11, 23; 4:7, 11, 12; 2 John 1:5 |
| "without affection" | Moses 7:33 | Romans 1:31; 2 Timothy 3:3 |
| "the Lamb is slain from the foundation of the world" | Moses 7:47 | Compare Revelation 13:8 – "the Lamb slain from the foundation of the world," as a noun phrase); the term "the Lamb" is used as a title of the Messiah only in the New Testament and is distinctively Johannine (John 1:29, 36; twenty-seven instances in Revelation), and the words lamb and slain collocate only in Revelation 5:6, 12; 13:8. |
| "climb up" by a gate or door, as a metaphor of progression through Christ | Moses 7:53 | John 10:1 |
Video by The Interpreter Foundation.
This language can be explained by a few possible factors, not all mutually exclusive.
The first possibility to consider is that Joseph Smith translated the Book of Moses into a vernacular that was comprehensible to his 19th century audience. Joseph's contemporaries were steeped in biblical language and used it even in everyday speech. The language of the New Testament was the natural way to discuss certain theological ideas.
D&C 1꞉24 tells us that in revelation, God uses the language of his audience to communicate effectively" Behold, I am God and have spoken it; these commandments are of me, and were given unto my servants in their weakness, after the manner of their language, that they might come to understanding."[21]
Another possibility is that the Book of Moses was originally written in an early Christian context. That would place the composition of the Book of Moses in the 1st and 2nd century AD (about 1900 to 1800 years ago). Calabro outlined and defended this theory.[20] Calabro argues that the Book of Moses can still preserve actual events from the life of Moses while placing the story in a Christian context describing it with Christian language. Thus, Joseph Smith could actually be restoring lost understanding of Moses—but that information has already been filtered through New Testament language.
One potential weakness of this theory is that it disrupts the understanding of many Church members about the Book of Moses, since it has more traditionally been seen as a restoration of Moses' writings in Genesis. However, Joseph Smith does not seem to have left a detailed account of what the Book of Moses represents. Joseph saw the JST as a restoration of "many important points touching the salvation of men, [that] had been taken from the Bible, or lost before it was compiled."[22]
This theory could also, in essence, be turned on its head, making an ancient version of the Book of Moses the source of subsequent Christian writing. Latter-day Saint author Jeff Lindsay and former BYU professor Noel Reynolds have theorized that the Book of Moses influenced the language of the Book of Mormon via the brass plates or another source.[23]
Speaking in reference to the Bible, the Book of Mormon has God announce that "I speak the same words unto one nation like unto another. And when the two enations shall run together the testimony of the two nations shall run together also."[24]
It is certainly possible that the same concepts were revealed to Moses with similar language as that used in the New Testament.
There are therefore multiple models which would explain the similarity between the Book of Moses and the New Testament. Given that the Book of Moses claims to be a translation, it is hardly strange that it would echo another translation (the KJV bible) that discusses the same ideas and issues.
The scriptures affirm that there is "One God" consisting of Father, Son, and Holy Ghost. A great debate in Christian history has been the nature of this oneness.
Protestant critics do not like the fact that Latter-day Saints reject the nonbiblical Nicene Creed, which teaches a oneness of substance. Latter-day Saints believe that God is one, but accept the Biblical witness that this is a oneness of purpose, intent, mind, will, and love, into which believers are invited to participate (see John 17꞉22-23). Thus, it is proper to speak of "God" in a singular sense, but Latter-day Saints also recognize that there is more than one divine person—for example, the Father and the Son.
This is not a contradiction; it merely demonstrates that the Latter-day Saints do not accept Nicene trinitarianism.
When God gives new insight and revelation, he doesn't typically "rewrite" all scripture that has gone before: He simply adds to it.
The creation account in the Book of Abraham supports a plurality of gods. Critics claim that the Bible does not support this. However, there are two errors in the assumption that the Bible does not support a plurality of gods.
Error #1: It is debatable that the unedited King James Version of Genesis truly only includes "one God." There are clearly multiple divine personages in Genesis:
And the LORD God said, Behold, the man is become as one of us, to know good and evil.... (Genesis 3꞉22)
Only creeds or convictions that insist on a single divine being make us unable to notice.
Error #2: The Joseph Smith Translation of Genesis actually did clarify the role and existence of multiple divine personages. The Book of Moses in the Pearl of Great Price (which is the simply the Joseph Smith Translation of Genesis) has many examples of multiple divine personages:
I have a work for thee, Moses, my son; and thou art in the similitude of mine Only Begotten; and mine Only Begotten is and shall be the Savior, for he is full of grace and truth; but there is no God beside me, and all things are present with me, for I know them all (Moses 1꞉6).
Moses looked upon Satan and said: Who art thou? For behold, I am a son of God, in the similitude of his Only Begotten; and where is thy glory, that I should worship thee? (Moses 1꞉13)
for God said unto me: Thou art after the similitude of mine Only Begotten....Call upon God in the name of mine Only Begotten, and worship me. (Moses 1꞉16-17)
Moses lifted up his eyes unto heaven, being filled with the Holy Ghost, which beareth record of the Father and the Son; (Moses 1꞉24)
And worlds without number have I created; and I also created them for mine own purpose; and by the Son I created them, which is mine Only Begotten. (Moses 1꞉33)
That's just the first chapter of the JST of Genesis. There are many, many more examples in Moses.
In chapter 2 of Moses, God prefaces his remarks by saying, "I am the Beginning and the End, the Almighty God; by mine Only Begotten I created these things; yea, in the beginning I created the heaven, and the earth upon which thou standest" (Moses 2꞉1).
So, in each case when "I, God" did something in the creation, it should be understood that the Only Begotten is also involved, since it is by him that God created all. So, there are multiple divine personages in each mention in the verses that follow.
Some critics have claimed that the Church is "embarrassed" by the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible. [25]
This claim is contradicted by an enormous amount of historical evidence. The claim was made in 1977. In 1978, the Church produced its new version of the KJV after years of work. Thus, the JST was the focus of serious attention by the Church long before the Tanners began to insist that leaders were ashamed of it.[26] It had multiple footnote and appendix entries from the JST.
The Church magazines also launched a concerted effort to introduce Latter-day Saints to the JST material that was now easily available, and to encourage its use. Some examples of this effort published around the time the Tanners were making their claim include:
The Church is not, and was not, embarrassed by the JST. In its historical context, the critics' claim is incredibly ill-informed.
Critical sources |
|
Parallel passages from the Book of Mormon and Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible sometimes disagree not only with the King James Version of the Bible, but also with each other. Critics ask why Joseph's earlier work (i.e., the Book of Mormon) generally followed the King James Version of the Bible closely while his later work (i.e., the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible) did not. Critics ask which translation did Joseph get right, implying that one is wrong, hence bringing his prophetic calling into question. Critics generally cite any of a number of passages from Matthew 5-7 from the King James Version and Joseph Smith Translation and 3 Nephi 12-14 from the Book of Mormon. A much celebrated example is:
Matthew 6:25-27 (King James Version)
3 Nephi 13꞉25-27) (Book of Mormon)
Matthew 6:25-27 (Joseph Smith Translation)
Joseph had different purposes in mind in his different translations. This is not unique or unusual in scripture—even the Bible. Hence, neither the Book of Mormon nor the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible can be discounted because of seeming discrepancies with each other or with the King James Version of the Bible.
Joseph Smith had different purposes in mind when bringing forth the Book of Mormon and the Joseph smith Translation. His purpose in bringing forth the Book of Mormon was to witness "the reality that "Jesus is the Christ, the Eternal God, manifesting himself unto all nations". Departing from the King James Version, i.e., the translation familiar to those who would become the Book of Mormon's first readers, would have been a stumbling block in achieving its purpose. On the other hand, Joseph's later purpose in bringing forth the Joseph Smith Translation is largely understood to have been one of redaction, or inspired commentary—to resolve confusion regarding biblical interpretation[27] Hence the different wording, and in some cases, even content.
Gleason Archer, well known Evangelical Christian and the Author of a highly respected book called "Encyclopedia of Bible Difficulties", addresses the issue of Paul citing deficient Greek Septuagint translations that appear in our New Testaments today in lieu of better translations of the Old Testament he could have come up with. Archer says:
Suppose Paul had chosen to work out a new, more accurate translation into Greek directly from Hebrew. Might not the Bereans have said in reply, "that’s not the way we find it in our Bible. How do we know you have not slanted your different rendering here and there in order to favor you new teaching about Christ?" In order to avoid suspicion and misunderstanding, it was imperative for the apostles and evangelists to stick with the Septuagint in their preaching and teaching, both oral and written.
We, like the first-century apostles, resort to these standard translations to teach our people in terms they can verify by resorting to their own Bibles, yet admittedly, none of these translations is completely free of faults. We use them nevertheless, for the purpose of more effective communication than if we were to translate directly from the Hebrew or Greek.[28]
Archer's point is that it is more important in certain settings that Paul's writings be familiar rather than 100% precise.
Key sources |
|
FAIR links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
Video published by BYU Religious Education.
|
Print |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Notes
The Church would never allow the Inspired Version of the Bible to be printed because it would tend to embarrass the church and to show that Joseph Smith was not a prophet of God.
The contents of the "Inspired Version" of the Bible contradict doctrines taught by the Mormon church.
Joseph Fielding Smith said that the King James Bible is "the best version translated by the power of man" and that the "Inspired Version" was never completed, yet Joseph Smith stated that he completed the translation of the Bible.Author's sources:
- Doctrines of Salvation, vol. 3, p.191
- History of the Church 1:324
- History of the Church 1:368
Joseph's "Inspired Version" of the Bible does not restore any of the "lost books" of the Bible.Author's sources:
- Joseph Smith's Revision of the Bible, p. 18
Notes

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now